What
is a Database?
The traditional definition of a database is a collection of related data
organized into fields, records and tables that has been created for a particular
purpose. Data is the basic information component. Data (such as a person's
last name or zip code) is stored in fields and related fields are organized
into records. Identically structured records are then collected into a
table. The data stored in this table can then be sorted and searched, and
useful information in the form of reports can be produced. As an example,
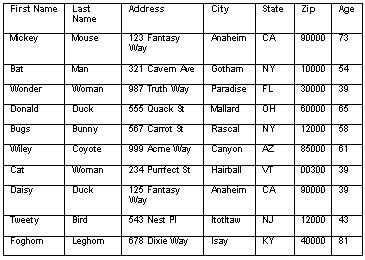
the table below contains fields for First Name, Last Name, Address, City,
State, Zip and Age, and each row contains the data for each field for a
particular individual.
FIGURE 1. Sample Table.
 |
The Access Database Management System
The concept of a database is more broadly defined within the Microsoft
Access 2000 environment. A Microsoft Access database not only consists
of data, fields, records, and tables but also includes those queries and
reports created as a result of manipulating those fields, records, and
tables. As such Microsoft Access is more than a tool used to store data
— it is a complete database management system (DBMS). Additionally, the
Microsoft Access 2000 DBMS can not only organize and manage a table of
records (sometimes called a flat file database) but can also manage and
organize many tables possessing common components into a relational database. |