
Document Markup | Document has meta tags | File > Properties |

Headings | - Heading styles give a document structure by category or topic (Heading 1 through 6).
- Heading 1: Document Title or a major section
- Heading 2: Major subsection titles
- Heading 3: Further subsection titles, and so forth
- Use of headings to ease navigation within a document.
- Headings allow for a table of contents to be generated automatically.
| Word - View tab
- Select Navigation Pane
PowerPoint: PowerPoint does not use headings instead of using slide title. Every slide should have meaning and unique title. If the same topic, add i.e. 1 of 3, 2 of 3, 3 of 3. |

Readability | - Avoid extremely long and wordy sections.
- Avoid unusual word, jargon, and acronyms as possible.
- Provide definition or explanation for abbreviation.
- Avoid center align paragraph.
- Use strong not bold; emphasis not italic.
- Use different visual elements such as color, fonts, spacing and imagery to increase readability.
| - Manually inspect whether the paragraph alignment (saccade reading behavior).
- Manually inspect the page to find repeated, unusual wording.
- Manually inspect the page to find abbreviation, acronyms or jargon without explanation.
- Manually inspect the page for any confusing wording, instructions that create confliction.
|

Images | - Images have descriptive alternative text.
- Be brief and descriptive.
- “Image of…” or “photo of…” or “graphic of…” is not needed.
- Images should have captions if the images convey complicated information, this will provide equal access to all users.
- Images should be visibly easy to comprehend (not pixilated, not too small, etc.)
- Limit the use of text as images.
| Review if images have alternative text. Right-click to select "Edit Alt Text” to see if images have descriptive alternative text. |

Color | - Select colors with deep contrast between the foreground and background.
- Provide captions if using color to convey meaning i.e. which section is highlighted in red?
| - Use the Colour Contrast Analyzer to ensure accessible contrast.
- Review the document to identify if only color is used to convey info.
|

Links | - Links should be clear and directly relate to the title or heading of the linked page.
- Use “Visit the Universal Design Center” instead of “Click here for more details.”
- Do not use the same link text to refer to different resources.
- Do not use different link text to refer the same resources.
| - Review all the links in the page.
- Visually verify that the following phrases are not used as links: Click Here, Read More, More, More information.
- Review the link text to make sure it is descriptive enough to understand where it will lead.
- Check to see if there are any link text’s that have the same text.
- Check the link to see if it leads to an active page.
- Best Practices for Accessible Links
|

Tables | - Use tables to organize data not format as layout.
- Tables are read from left to right, top to bottom.
- Do not create table using the Draw Table Tool.
- Avoid merged, split, or blank cells.
- If data tables are present in document, they must have:
- Provide title (i.e. Caption) and Summary
- Heading cells for columns or rows
| - Title your table using the Caption tool
- Right click to select Insert Caption or
- Go to References tab, then select Insert Caption
- In the popup window, type the title of the table in the Caption textbox
- In the Label textbox, select Table
- Position textbox, select Above selected item then select OK
- Table Header Cells
- Table tools added to the Ribbon when Table is created or selected
- Header checkboxes found under Design tab
- Header Row (Column headers)
- First Column (Row Headers)
If ‘Repeat as header row at the top of each page’ isn’t selected, table headers will be ignored when exporting as a PDF and won’t be read by screen reader. - Right-click the first row of the table and select Table Properties.
- On the Row tab, make sure the checked Repeat as header row at the top of each page and unchecked Allow row to break across pages. Click OK.
- Repeat these steps for all tables in the document. Save the document.
Visit Guide for Creating Accessible Table (pdf) |
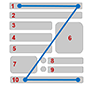
Reading Order | Screen readers read a document from left-to-right and up-to-down. That means reading order is important for users with visual impairments. When content, tables, images or charts is out of order or a document is poorly organized, the reader can become confused to the meaning of the information. The reading order should be the same as visual order for English language. | Word: Logical reading order: Read information from left to right and from top to bottom. PowerPoint: To check or fix reading order, select Home > Arrange > Selection Pane. Reading order is shown in reverse, bottom to top in the Selection pane. |

Multimedia | Videos, captured lectures, recorded presentations for instructional media must all have captions.- Videos embedded in Microsoft Office are not accessible when the file is converted to Acrobat PDF. The video becomes an image.
- Embedded videos are not accessible to screen reader users or users navigating with a keyboard or some other navigation device other than a mouse.
- An alternative put the link of the video underneath the video itself.
| |
 Accessibility Checker Accessibility Checker
| The checker will scan for errors and provide tips on how to fix them. Use the built-in Accessibility Check in Microsoft Office. | Review tab > Check Accessibility button PowerPoint: Use Outline View for a quick check of text accessibility. Ensure title and body text are identified correctly in each slide. Microsoft Office Accessibility Checker guide |










 Accessibility Checker
Accessibility Checker