Experiments under CPU-intensive Workload
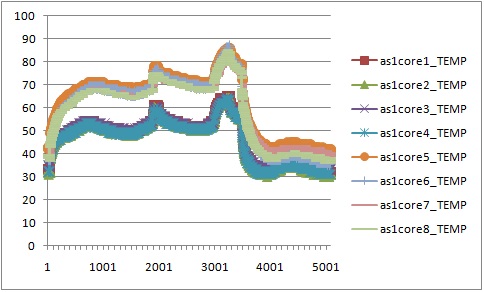
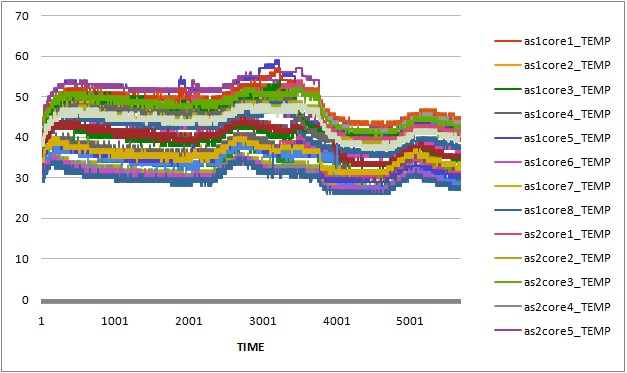
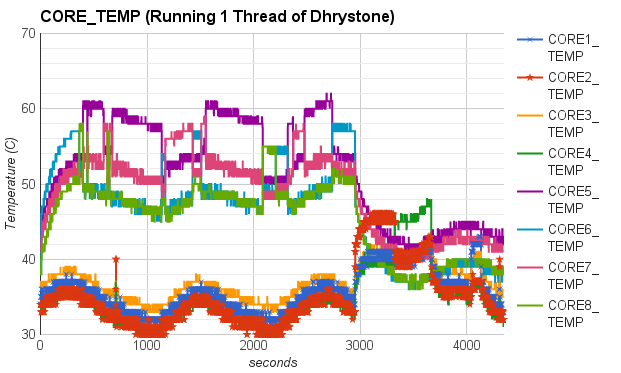
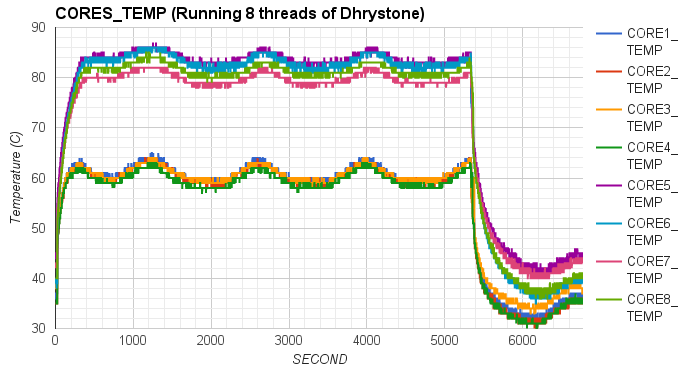
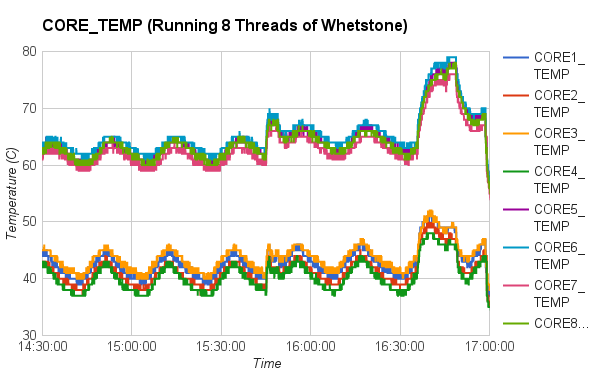
Whetstone and Dhrystone were used to generate floating point operations and integer operations in our experiments. The experimental data showed that CPU temperature increased around 40 degrees Celsius when all CPU cores were running under heavy workload. It took around half an hour to an hour for those CPU cores to reach maximum steady temperature, and around 4 to 16 minutes to cool down to room temperature.
In particular, we first compared the impact of integer operations and floating point operations on CPU temperature. We set up two groups of experiments executing either Whetstone or Dhrystone, respectively. In each group, the benchmark tool was executed in a single-thread process and a eight-thread process. From the results, we found that running integer computation (Dhrystone) in single thread resulted in higher increment in CPU temperature than executing floating point computation (Whetstone) in single thread. Similar results were observed when running Dhrystone or Whetstone in eight threads.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
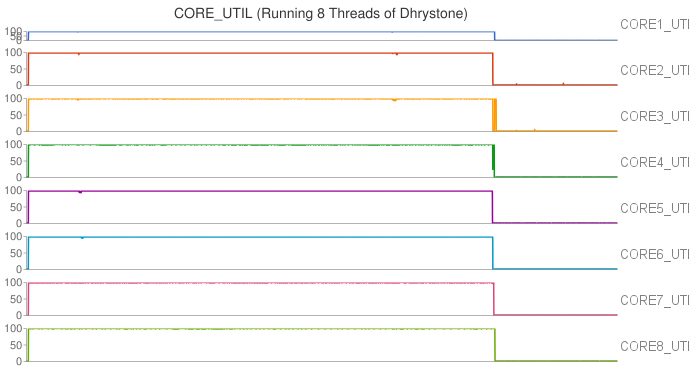 |
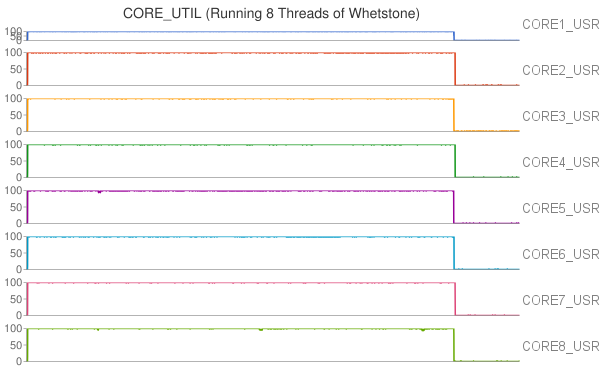 |
(These eight figures were created by Wilson Lin.)
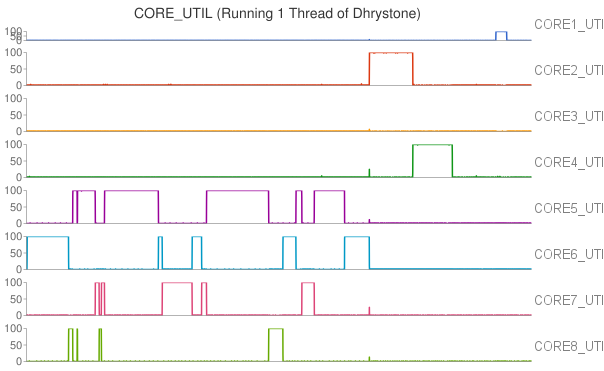
Moreover, we also observed that the thread migrated among CPU cores when running Whetstone in single thread. To further study the thread migration problem, we conducted one more group of experiments by running Whetstone in more threads. Each thread drove a CPU core to full utilization. The results of the experiments can be found at Two threads, Three threads, Five threads, Eight threads, Nine threads.
In our cluster, each processor has 8 cores in two core groups. From the experimental results, we found that workload was first assigned to any core in a particular group with relatively lower temperature, and the workload would migrate among these cores at any time. If all the cores in the group were fully utilized, new workload or tasks would be assigned to any cores in other groups.
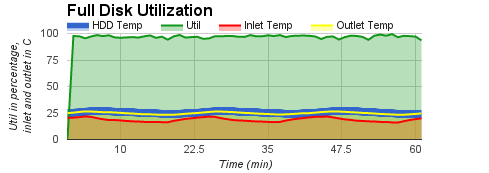
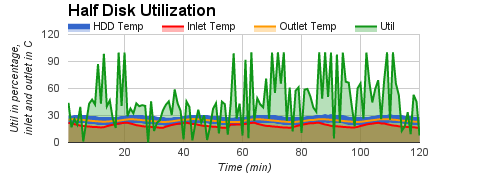
We also conducted three groups of experiments, in which CPU utilization was kept at low level, anywhere between low and moderate level, or anywhere between moderate and high level. The experimental results are shown in
| temperature under low CPU utilization, | temperature under low or moderate CPU utilization, | temperature under moderate or high CPU utilization. |