24.2.3 – Teaching to multiple intelligences
"Intelligence is an umbrella term used to describe a property of the mind that encompasses many related abilities, such as the capacities to reason, to plan, to solve problems, to think abstractly, to comprehend ideas, to use language, and to learn. There are several ways to define intelligence. In some cases, intelligence may include traits such as creativity, personality, character, knowledge, or wisdom." Wikipedia
Multiple Intelligences
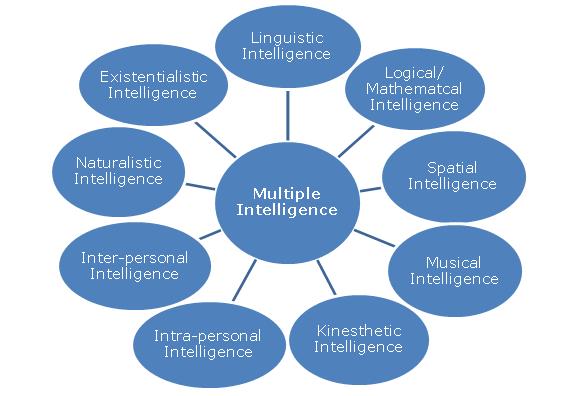
Intelligence is a property of the mind that includes many related abilities such as the capacities to reason, plan, solve problems, comprehend language and ideas, learn new concepts, and think abstractly. Historically, psychometricians have measured intelligence with a single score (intelligence quotient, IQ) on a standardized test, finding that such scores are predictive of later intellectual achievement. Howard Gardner and others assert that there are multiple intelligences, and that no single score can accurately reflect a person’s intelligence. More importantly, the theory of multiple intelligences implies that people learn better through certain modalities than others, and that the science teacher should design curriculum to address as many modalities as possible. Gardner identifies seven intelligences, which are listed below. The numbers in parentheses indicate sections in this book that address each intelligence.
- Logical /Mathematical Intelligence is used when thinking conceptually (6.1-4, 7.1-7, 10.1-5, 13.9, 16.1-6, 18.1-3), computing (14.1-3, 15.1-7, 17.1-7, 20.1, 20.8), looking for patterns (1.1-4,16.4, 16.6, 17.5-7), and classifying (8.1-6, 19.1-5)
- Linguistic/Language Intelligence is used when learning by listening (21.1), verbalizing (1.1-4, 3.1-4, 11.2-4, 22.6), reading (2.1-4), translating (14.1-3), and discussing (8.6, 22.4).
- Naturalist Intelligence is used to question (5.1, 22.1, 23.1), observe (5.2-3, 22.2), investigate (23.2), and experiment (5.1-10, 23.3-4).
- Visual / Spatial Intelligence is used when learning with models (12.1-5), photographs (16.4, 16.6), videos (16.5), diagrams (8.1-6, 16.1-3, 20.2-7), maps (21.1-7) and charts (20.2-7).
- Bodily kinesthetic intelligence is used to process knowledge through bodily sensations (12.2), movements (12.2), physical activity (labs in companion volumes, Hands-on Chemistry and Hands-on Physics), and manipulation (22.2).
- Interpersonal Intelligence is used when learning through cooperative learning experiences (22.3, 22,5), group games (13.1-8), group lab work (22.5), and dialog (8.6, 23.4).
- Intrapersonal Intelligence is used when learning through self-dialog (7.1-3,11.1), studying (11.2-4) and self-assessment (7.4-7).
- Musical Intelligence is used when learning through rhythm, melody, and non-verbal sounds in the environment (24.8).